
With the successful convening of the mobile world congress 2019MWC in Barcelona, Spain, major mobile phone manufacturers have also launched their own 5G new products, causing a hot discussion in the network industry.
The network innovation of modern science and technology can change the operation mode of many industries, and even directly change our way of life. Network technology is no longer distant and strange to us. Today, Ebyte will take you to "LoRa", "Zigbee", "WIFI", "nb - iot", "bluetooth", the current commonly used wireless communication technology, to understand what kind of service they provide for our data transmission in various occasions.
Some people may ask, "why are there so many different wireless technologies, and what's the difference?" Now, let's take a brief look at some common networking methods for the Internet of Things.
LoRa(long range) is a technology developed by Semtech that typically operates at 915MHz in the United States, 868MHz in Europe, and 433MHz in Asia. The physical layer (PHY) of LoRa uses a unique form of FM chirped spread spectrum technology with forward error correction (FEC). This spread spectrum modulation allows multiple radio devices to use the same frequency band as long as each device USES a different chirp and data rate. The typical range is 2km to 5km, with a maximum range of 15km, depending on the location and antenna characteristics.
ZigBee is an ideal choice for the Internet of Things. Although ZigBee generally works in the 2.4ghz ISM frequency band, it can also be used in the frequency band of 902MHz to 928MHz and 868MHz. In the 2.4ghz band, the data rate is 250kb/s. It can be used in point-to-point, star, and grid configurations, supporting up to 216 nodes. As with other technologies, security is guaranteed through aes-128 encryption. A major advantage of ZigBee is that it has pre - developed software application configuration files for specific applications (including the Internet of things). The final product must be licensed.
Wi - fi is widely used in many iot applications, most commonly as a link from a gateway to a router connected to the Internet. However, it is also used for major wireless links requiring high speed and medium range.
Most wi - fi versions work in the 2.4ghz license - free band and can transmit up to 100m, depending on the application. The popular 802.11n can reach speeds of up to 300Mb/s, while newer 802.11ac, which works in the 5GHz ISM band, can even exceed 1.3gb /s.
A new version of wifi, called HaLow, will be available for iot applications. This version, code - named 802.11ah, USES a licensed frequency band of 902MHz to 928MHz in the United States and similar bands of 1GHz or less in other countries. While most wifi devices have a maximum coverage of 100 meters under ideal conditions, HaLow can reach up to 1 kilometer with the right antenna. The modulation technology of 802.11ah is OFDM, which USES 24 subcarriers in 1MHz channel and 52 subcarriers in the channel with larger bandwidth. It can be BPSK, QPSK, or QAM, thus providing a wide range of data rates. In most cases a rate of 100kb/s to several megabytes /s is sufficient - the real goal is low power consumption.
Another new wifi standard for iot applications is 802.11af. It is designed to use TV white space or unused channels ranging from 54MHz to 698MHz. These channels are well suited for long distance and non-line-of-sight transmission. The modulation technology is OFDM using BPSK, QPSK or QAM. The maximum data rate per 6MHz channel is approximately 24Mb/s, although longer distances are expected in the lower VHF TV band.
Narrow Band Internet of Things (NB - IoT) has become an important branch of the Internet of everything. Nb - iot is built on cellular networks and consumes only about 180KHz of bandwidth. It can be deployed directly on GSM, UMTS, or LTE networks to reduce deployment costs and achieve smooth upgrades.
Nb - iot is an emerging technology in the field of IoT that supports cellular data connectivity of low - power devices over wide area networks (wans), also known as low power wide area networks (lpwans). Nb - iot supports efficient connectivity for devices with long standby times and high network connectivity requirements. Nb - iot devices are said to provide at least 10 years of increased battery life while also providing very comprehensive coverage of indoor cellular data connections.
Bluetooth is a wireless transmission technology that can theoretically connect devices up to a distance of about 100 meters, but only about 10 meters in practice. Its biggest feature is that it enables portable mobile communication devices and computers to connect to the Internet without cables and transmit data and information. It is now widely used in the connection between smart phones and smart wearable devices, as well as smart home, vehicle Internet of things and other fields. The new bluetooth 5.0 can not only be compatible with older versions, but also bring the advantage of faster and longer transmission distance.
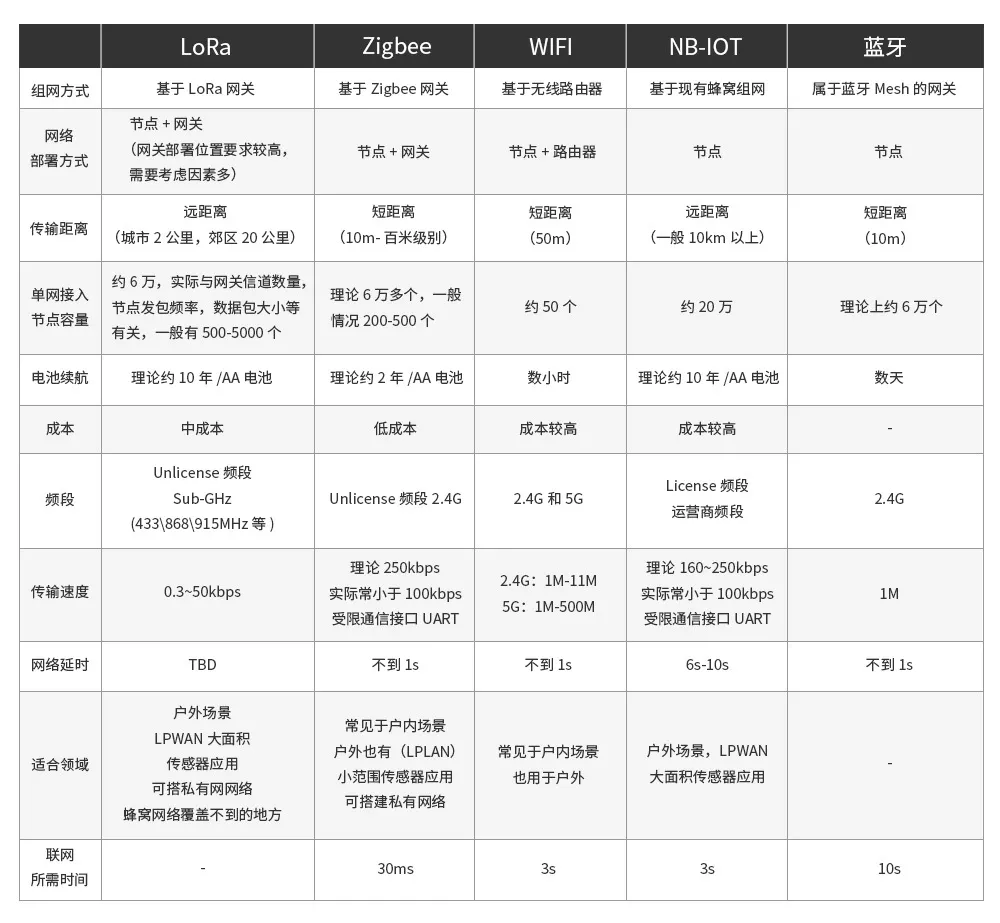
Through the above comparison, do you have a simple and intuitive understanding of these five wireless communication technologies? Are you eager to try some related products, but don't know how to choose reliable products? Please visit official website for details or go to alibaba to search chengdu ebyte official store.